Overview
ViroMag R/L Transduction Reagent is a magnetic nanoparticles formulation optimized for Retroviruses and Lentiviruses. Based on the Magnetofection™ technology, this reagent allows concentrating the complete applied dose of Retro/Lentiviral particles onto cells within minutes, inducing a significant improvement of virus infectivity with extremely low vector doses. Due to its specific properties, ViroMag R/L is ideal to infect non permissive cells. This reagent demonstrates an exceptionally high efficiency to promote, control and assist viral transductions in a so that no molecular biology processes or biochemical modifications are required.
-
Increase transduction efficiency
-
Accelerate the transduction process
-
Efficient for hard-to-infect and non-permissive cells
-
Concentrate the viral dose onto the cells
-
Suitable for all type of Retro/Lentivirus
-
Synchronise cells adsorption/infection without modifications of the viruses
"Use of ViroMag R/L to knock down a gene by CRISPR/Cas9-guided genome editing with Lentivirus in THP-1 cells"
Safronova A et al, Nature Immuno. 2018
"The magnetofection beads have been a game-changer for the transduction efficiency of our lentiviruses. We are using very hard to transduce B-lymphoblastomas that grow in suspension and viral concentration using filtering in conjunction with ViroMag R/L has brought our efficiency up from about 2% to 70-80%. High transduction efficiency on mammary epithelial organoids in suspension"
Erna Magnúsdóttir - University of Iceland
Sizes:
-
100 µL 30-500 transductions in 96-well plate
-
200 µL 60-1,000 transductions in 96 well plate
-
1 mL 300-5,000 transductions in 96-well plate
-
#KC30700: ViroMag R/L Starting Kit with Super Magnetic plate + 200µL of ViroMag R/L
-
#KC30796 : ViroMag R/L Starting Kit with plate 96 magnets + 200µL of ViroMag R/L
-
#KC30600: ViroMag Triple Starting Kit with Super Magnetic plate + 100 µL of ViroMag, AdenoMag, ViroMag RL
-
#KC30696 : ViroMag Triple Starting Kit with plate 96 magnets + 100 µL of ViroMag, AdenoMag, ViroMag RL
Storage: +4°C
Shipping Conditions: Room Temperature
| CATALOG NUMBER |
UNIT SIZE |
| RL40100 |
100 µL
|
| RL40200 |
200 µL
|
| RL41000 |
1 mL
|
| KC30700 |
ViroMag R/L Starting Kit
|
| KC30796 |
ViroMag R/L Starting kit plate 96 magnets
|
| KC30600 |
ViroMag Triple Starting Kit
|
| KC30696 |
ViroMag Triple Starting Kit with plate 96 magnets
|
Applications
-
Perfect for cell transduction with all retroviral and lentiviral vectors especially VSV-G pseudoviruses.
-
Suitable for mammalian cells: Cell lines, primary cells, hard to transfect.
RECOMMENDED FOR: Enhancing and synchronizing retro- and lentiviruses transductions.
Results
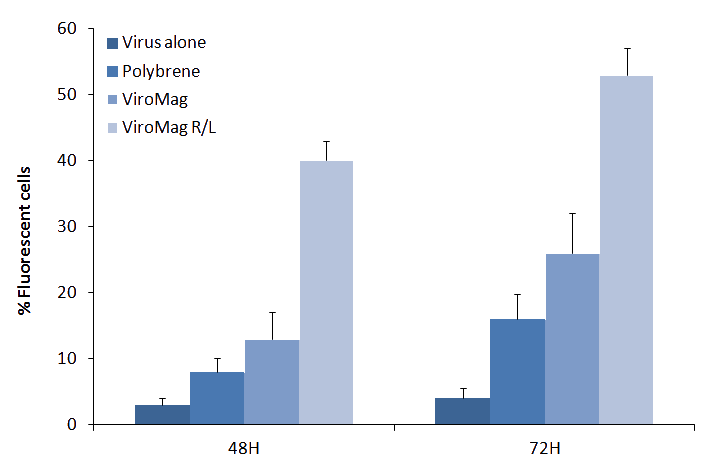
Figure 1: ViroMag R/L is highly efficient for lentiviral infection. NIH-3T3 were infected with a lentivirus coding for GFP alone or with Polybrene, ViroMag and ViroMag R/L. Percentage of infected cells was determined 48 and 72H after infection by FACS analysis.
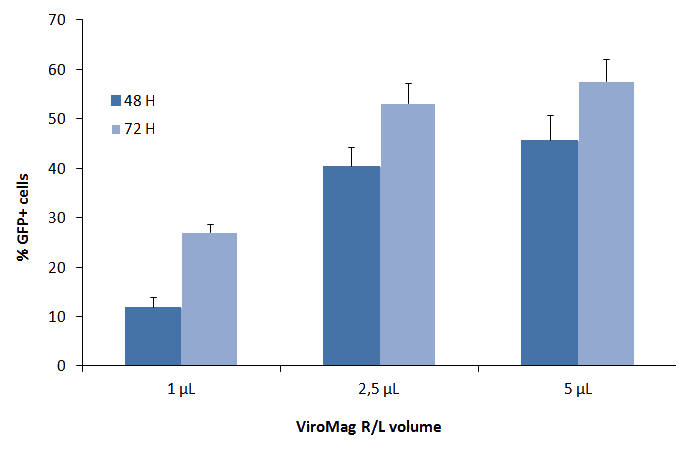
Figure 2: ViroMag R/L is highly efficient in a dose dependent manner. NIH-3T3 were infected with a lentivirus coding for GFP in presence of several doses of ViroMag R/L. Percentage of infected cells was determined 48 and 72H after infection by FACS analysis.

 SingaporeSG
SingaporeSG ChinaCN
ChinaCN MalaysiaMY
MalaysiaMY IndonesiaID
IndonesiaID MyanmarMM
MyanmarMM_pddqnqv8.png)




_7k6wa19e.jpg)
_zu3kfeaj.jpg)
_qye2acj3.jpg)
_vspgyc0k.jpg)
_yq8hv96j.jpg)