Overview
HeLaFect is a transfection reagent specifically developed for HeLa cell lineage transfection with high efficiency. HeLaFect is a lipid-based reagent based on the Tee-Technology (“Triggered Endosomal Escape”). The cationic design of HeLaFect reagent allows high nucleic acid compaction for an efficient transport into HeLa cells. This reagent is composed of biodegradable lipids leading to high viability and is ready-to-use.
HeLaFect transfection reagent benefits:
- Highly efficient: more than 80% of transfected HeLa cells
- Ready-to-use: no need for additional buffer
- Low nucleic acid amount - minimized toxicity
- High level of nucleic acid compaction
- Easy and straightforward protocol
-
Compatible with any culture medium: medium change not required
Sizes:
-
500µL: 125-250 transfections with 1µg of DNA
-
1mL: 250-500 transfections with 1µg of DNA
-
5mL: 1250-2500 transfections with 1µg of DNA
Storage: -20°C
Shipping Conditions: Room Temperature
| CATALOG NUMBER |
UNIT SIZE |
| HF20500 |
500 µL
|
| HF21000 |
1 mL
|
| HF25000 |
5 mL
|
Applications
RECOMMENDED APPLICATIONS: Nucleic acids transfection into HeLa cells.
Results
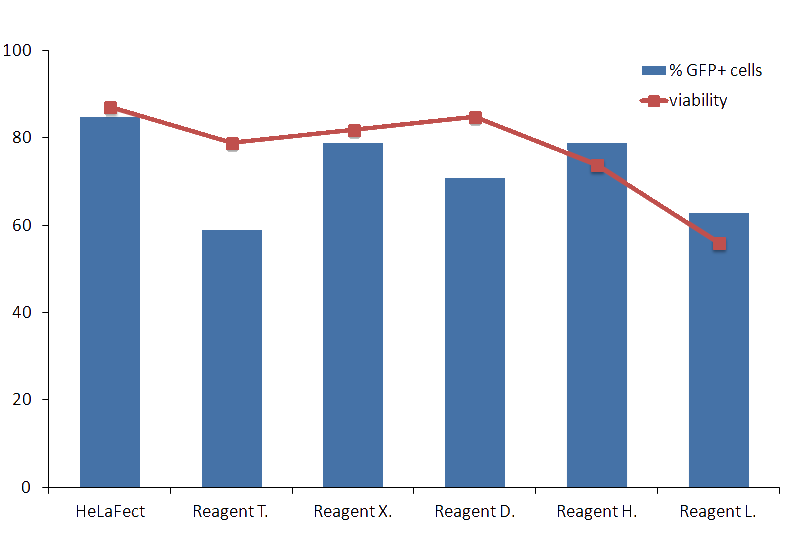
Figure1: Complexes of DNA and HeLaFect were prepared with 0.5 μg per well in a 24-well plate at a 2:1 ratio, and DNA transfections with other commercial transfection reagents were performed as recommended by the manufacturers. 24 h after, transfection efficiency was measured by FACS analysis and fluorescence microscopy.

 SingaporeSG
SingaporeSG ChinaCN
ChinaCN MalaysiaMY
MalaysiaMY IndonesiaID
IndonesiaID MyanmarMM
MyanmarMM_pddqnqv8.png)



_8gm06cr4.jpg)
_qorrcy9a.jpg)
_icakuykm.jpg)
_9bu7yv5n.jpg)